Install across Multiple Clusters
LLMariner deploys Kubernetes deployments to provision the LLM stack. In a typical configuration, all the services are deployed into a single Kubernetes cluster, but you can also deploy these services on multiple Kubernetes clusters. For example, you can deploy a control plane component in a CPU K8s cluster and deploy the rest of the components in GPU compute clusters.
LLMariner can be deployed into multiple GPU clusters, and the clusters can span across multiple cloud providers (including GPU specific clouds like CoreWeave) and on-prem.
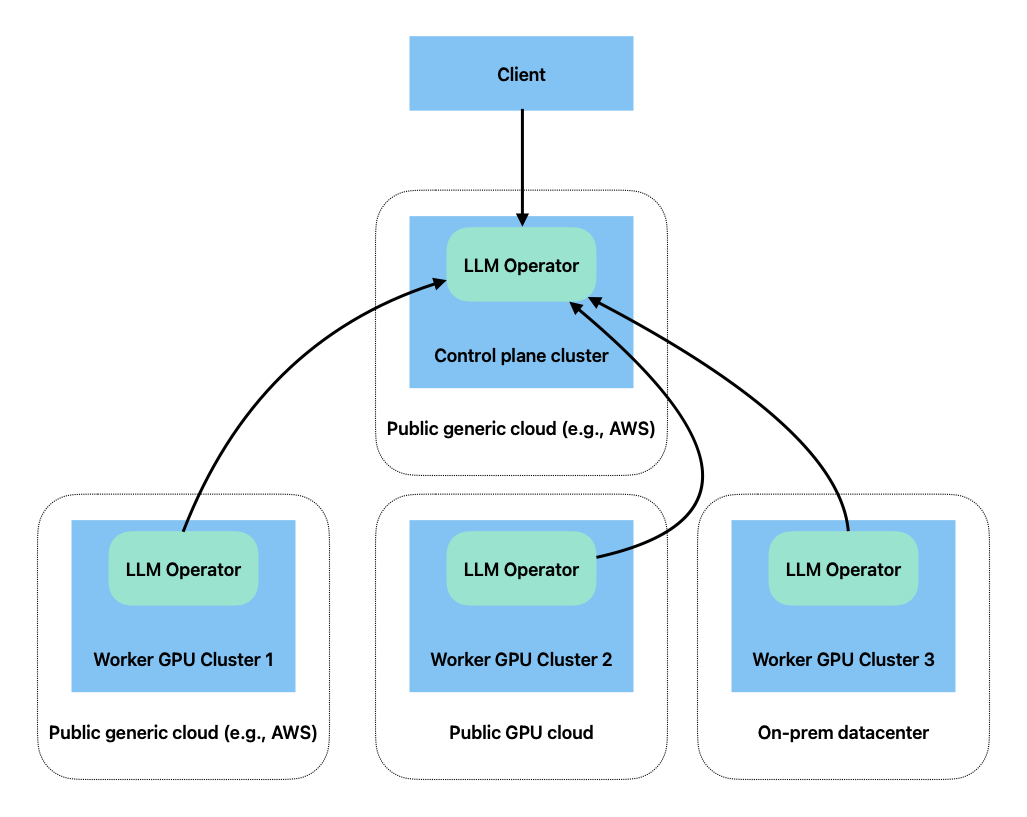
Deploying Control Plane Components
You can deploy only Control Plane components by specifying additional parameters the LLMariner helm chart.
In the values.yaml, you need to set tag.worker to false, global.workerServiceIngress.create to true, and set other values so that an ingress and a service are created to receive requests from worker nodes.
Here is an example values.yaml.
tags:
worker: false
global:
ingress:
ingressClassName: kong
controllerUrl: https://api.mydomain.com
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt
konghq.com/response-buffering: "false"
# Enable TLS for the ingresses.
tls:
hosts:
- api.llm.mydomain.com
secretName: api-tls
# Create ingress for gRPC requests coming from worker clusters.
workerServiceIngress:
create: true
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt
konghq.com/protocols: grpc,grpcs
workerServiceGrpcService:
annotations:
konghq.com/protocol: grpc
# Create a separate load balancer for gRPC streaming requests from inference-manager-engine.
inference-manager-server:
workerServiceTls:
enable: true
secretName: inference-cert
workerServiceGrpcService:
type: LoadBalancer
port: 443
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: inference.llm.mydomain.com
# Create a separate load balancer for HTTPS requests from session-manager-agent.
session-manager-server:
workerServiceTls:
enable: true
secretName: session-cert
workerServiceHttpService:
type: LoadBalancer
port: 443
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: "nlb"
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: session.llm.mydomain.com
Deploying Worker Components
To deploy LLMariner to a worker GPU cluster, you first need to obtain a registration key for the cluster.
llma admin clusters register <cluster-name>
The following is an example command that sets the registration key to the environment variable.
REGISTRATION_KEY=$(llma admin clusters register <cluster-name> | sed -n 's/.*Registration Key: "\([^"]*\)".*/\1/p')
The command generates a new registration key.
Then you need to make LLMariner worker components to use the registration key when making gRPC calls to the control plane.
To make that happen, you first need to create a K8s secret.
REGISTRATION_KEY=clusterkey-...
kubectl create secret generic \
-n llmariner \
cluster-registration-key \
--from-literal=regKey="${REGISTRATION_KEY}"
The secret needs to be created in a namespace where LLMariner will be deployed.
When installing the Helm chart for the worker components, you need to specify addition configurations in values.yaml. Here is an example.
tags:
control-plane: false
global:
objectStore:
s3:
endpointUrl: <S3 endpoint>
region: <S3 regiona>
bucket: <S3 bucket name>
awsSecret:
name: aws
accessKeyIdKey: accessKeyId
secretAccessKeyKey: secretAccessKey
worker:
controlPlaneAddr: api.llm.mydomain.com:443
tls:
enable: true
registrationKeySecret:
name: cluster-registration-key
key: regKey
inference-manager-engine:
inferenceManagerServerWorkerServiceAddr: inference.llm.mydomain.com:443
job-manager-dispatcher:
notebook:
llmarinerBaseUrl: https://api.llm.mydomain.com/v1
session-manager-agent:
sessionManagerServerWorkerServiceAddr: session.llm.mydomain.com:443
model-manager-loader:
baseModels:
- <model name, e.g. google/gemma-2b-it-q4_0>